Charles Darwin
Research
Until recently the great majority of naturalists believed that species were immutable productions, and had been separately created. This view has been ably maintained by many authors. Some few naturalists, on the other hand, have believed that species undergo modification, and that the existing forms of life are the descendants by true generation of pre-existing forms. Passing over allusions to the subject in the classical writers, the first author who in modern times has treated it in a scientific spirit was Buffon. But as his opinions fluctuated greatly at different periods, and as he does not enter on the causes or means of the transformation of species, I need not here enter on details.
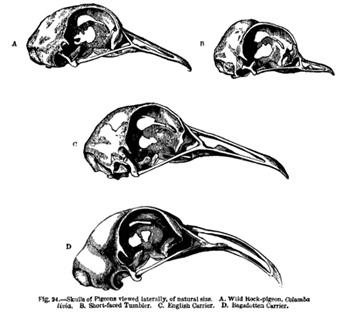
Skulls of pigeons viewed laterally, of natural size
Lamarck was the first man whose conclusions on the subject excited much attention. This justly-celebrated naturalist first published his views in 1801; he much enlarged them in 1809 in his "Philosophie Zoologique,' and subsequently, in 1815, in the Introduction to his "Hist. Nat. des Animaux sans Vertébres.' In these works he upholds the doctrine that species, including man, are descended from other species. He first did the eminent service of arousing attention to the probability of all change in the organic, as well as in the inorganic world, being the result of law, and not of miraculous interposition. Lamarck seems to have been chiefly led to his conclusion on the gradual change of species, by the difficulty of distinguishing species and varieties, by the almost perfect gradation of forms in certain groups, and by the analogy of domestic productions. With respect to the means of modification, he attributed something to the direct action of the physical conditions of life, something to the crossing of already existing forms, and much to use and disuse, that is, to the effects of habit.
Select Publications
- Dulcis, D., Jamshidi, P., Leutgeb, S. and Spitzer, N.C. (2013) Neurotransmitter switching in the adult brain regulates behavior. Science 340: 449-453.
- Plazas, P.V., Nicol, X. and Spitzer, N.C. (2013) Activity-dependent competition regulates motor neuron axon pathfinding via PlexinA3. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 110: 1524-1529.
- Spitzer, N.C. (2012) Activity-dependent neurotransmitter respecification. Nature Reviews Neurosci. 13: 94-106.
- Nicol, X., Hong, K.P. and Spitzer, N.C. (2011) Spatial and temporal second messenger codes for growth cone turning. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 108: 13776-13781.
- Velázquez-Ulloa, N.A., Spitzer, N.C. and Dulcis, D. (2011) Context-dependent dopamine specification by calcium activity across the central nervous system. J. Neurosci. 31: 78-88.

