Joseph Pogliano
Research
Evolution of the microbial cytoskeleton
Prokaryotic cells have a complex subcellular organization but how this organization is established and maintained remains poorly understood due to our limited knowledge of the proteins that make up the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. The goals of my lab are to identify and characterize the major families of dynamic cytoskeletal proteins that exist in bacteria, to determine the various functions that they perform, and to understand how these polymers are regulated spatially and temporally by other factors within the cell. My lab specializes in using genetics and cell biology to study the function and in vivo assembly dynamics of cytoskeletal polymers in many different species of prokaryotes, including E. coli, Bacillus subtillis, B. megaterium, B. thuringiensis, Mycobacterium smegmatis, and Pseudomonas species. Our approach has been to focus on bacterial plasmids as tools to discover new families of cytoskeletal polymers. Plasmids offer the advantages that they are genetically diverse and each encodes its own segregation system. Our studies have led to the discovery of new types of cytoskeletal structures involved in DNA segregation in bacteria (Pogliano 2008), including a new family of tubulins (TubZ) (Larsen et al. 2007) and a new family of actins (AlfA) (Becker et al. 2006). To complete some of our long term goals, we have initiated collaborations with biochemists, structural biologists and physicists to study polymer assembly in vitro and in silico to generate an integrated and detailed mechanistic understanding of cytoskeletal dynamics in prokaryotes. Studies of the bacterial cytoskeleton will lead to an understanding of how prokaryotic cells generate and maintain their subcellular organization and will provide insight into how the eukaryotic cytoskeleton evolved.
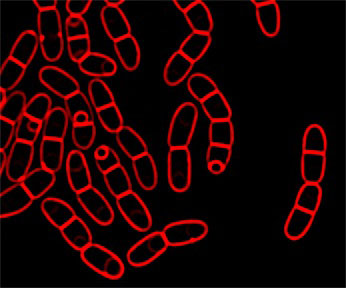
Image of sporulating Bacillus megaterium with membranes stained red with FM 4-64.
Select Publications
- Kraemer JA, Erb ML, Waddling CA, Montabana EA, Zehr EA, Wang H, Nguyen K, Pham DS, Agard DA, Pogliano J. A phage tubulin assembles dynamic filaments by an atypical mechanism to center viral DNA within the host cell. Cell. 2012 Jun 22;149(7):1488-99.
- Pogliano, J., Pogliano, N. and Silverman, J. Daptomycin mediated reorganization of membrane architecture causes mislocalization of essential cell division proteins J Bacteriol. September 2012 vol. 194 no. 17: 4494-4504. PMID: 22661688.
- Sakoulas G, Bayer AS, Pogliano J, Tsuji BT, Yang SJ, Mishra NN, Nizet V, Yeaman MR, Moise PA. Ampicillin Enhances Daptomycin- and Cationic Host Defense Peptide-Mediated Killing of Ampicillin- and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium. (2012) Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Feb;56(2):838-44. Epub 2011 Nov 28.
- Derman AI, Nonejuie P, Michel BC, Truong BD, Fujioka A, Erb ML, Pogliano J. Alp7R regulates expression of the actin-like protein Alp7A in Bacillus subtilis. (2012) J Bacteriol. May;194(10):2715-24. Epub 2012 Mar 16.
- Eswaramoorthy, P., Erb, M., Gregory, J., Silverman, J. Pogliano,K., Pogliano,J., Ramamurthi, K. Cellular architecture mediates DivIVA ultrastructure and regulates Min activity in Bacillus subtilis. (2011) mBIO 2011 Nov-Dec; 2(6): e00257-11.
- Purdy Drew KR, Pogliano J. Dynamic instability-driven centering/segregating mechanism in bacteria. (2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 5;108(27):11075-80. Epub 2011 Jun 17. PMCID:21685333
- Abhay Dhand, Arnold S. Bayer, Joe Pogliano, Soo-Jin Yang, Michael Bolaris, Victor Nizet, Guiquing Wang, and George Sakoulas Use of Anti-Staphylococcal b-Lactams to Increase Daptomycin Activity in Eradicating Persistent Bacteremia Due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Role of Enhanced Daptomycin Binding. (2011) Clinical and Infectious Disease, 53(2):p.158-163.
- Eloe EA, Malfatti F, Gutierrez J, Hardy K, Schmidt WE, Pogliano K, Pogliano J, Azam F, Bartlett DH. Isolation and characterization of a psychropiezophilic alphaproteobacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Nov;77(22):8145-53. Epub 2011 Sep 23. PMID: 21948832
- Liu WT, Yang YL, Xu Y, Lamsa A, Haste NM, Yang JY, Ng J, Gonzalez D, Ellermeier CD, Straight PD, Pevzner PA, Pogliano J, Nizet V, Pogliano K, Dorrestein PC. (2010) Imaging mass spectrometry of intraspecies metabolic exchange revealed the cannibalistic factors of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. Sep 14; 107(37):16286-90.
- Derman, A.I., Truong, B., Becker, E., Fujioka, A., Tucy, T.M. Erb, M., Patterson, P. and Pogliano, J. Phylogenetic analysis identifies many uncharacterized actin-like proteins (Alps) in bacteria: regulated polymerization, dynamic instability and treadmilling in Alp7A. (2009) Mol Microbiol. Aug;73(4):534-52.
- Pogliano J. (2008) The Bacterial Cytoskeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 20:19-27.
- Derman, AI, Lim-Fong, G., Pogliano J. (2008) Intracellular mobility of plasmid DNA is limited by the ParA family of partitioning proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 67:935-946.
- Larsen RA, Cusumano C, Fujioka A, Lim-Fong G, Patterson P, and Pogliano J. (2007) Treadmilling of a prokaryotic tubulin-like protein, TubZ, required for plasmid stability in Bacillus thuringiensis. Genes & Dev. Jun 1;21(11):1340-52.
- Becker E, Herrera NC, Gunderson FQ, Derman AI, Dance AL, Sims J, Larsen RA, Pogliano J. (2006) DNA segregation by the bacterial actin AlfA during Bacillus subtilis growth and development. EMBO J. 13;25(24):5919-31.

