Biologists Pinpoint Key Factor in Immune System Response to Viral Infection
Scientists identified the zip-1 gene as a first-line defense hub in worms
January 26, 2022
By Mario Aguilera
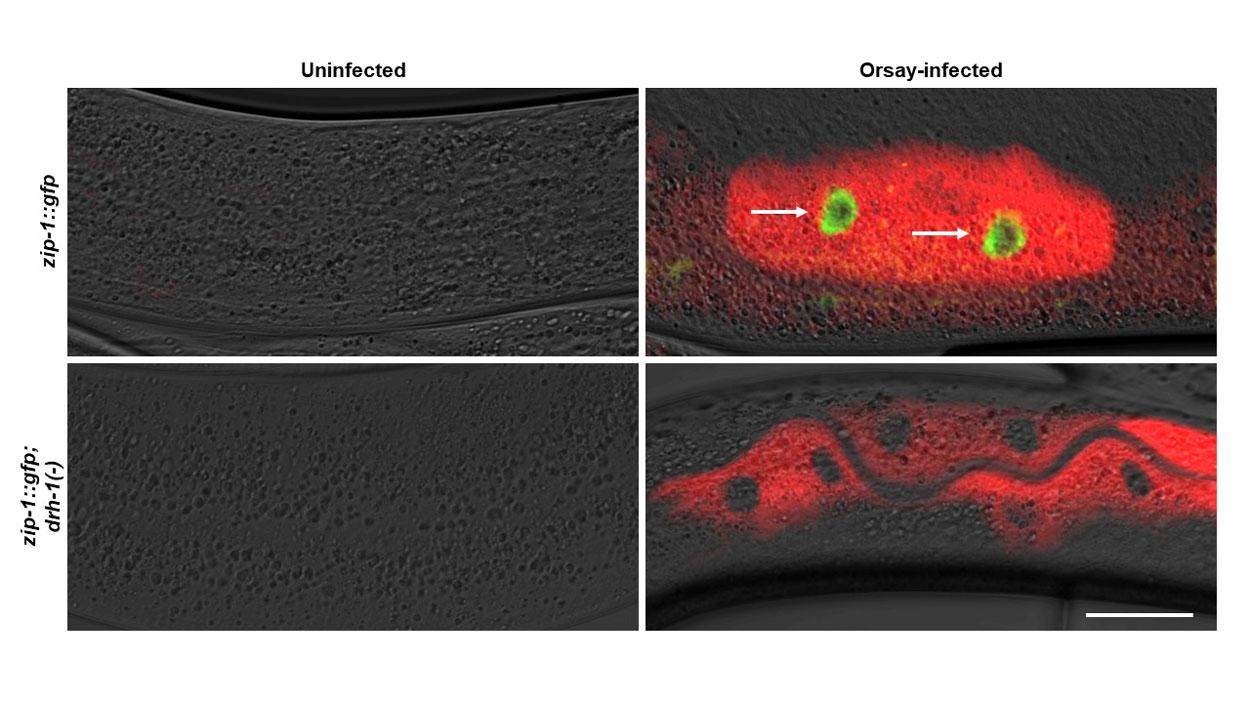
During the study, UC San Diego researchers used fluorescence to track viral infection. The image shows roundworm intestinal cells infected with Orsay virus (red) and ZIP-1 protein expression (green, indicated with arrows) that is induced only in the presence of the DRH-1 receptor.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the urgency for science to continue unraveling how viruses infect and how immune systems respond to such threats.
University of California San Diego researchers studying how small worms defend themselves against pathogens have discovered a gene that acts as a cell's first-line response against infection. Division of Biological Sciences Postdoctoral Scholar Vladimir Lažetić, Professor Emily Troemel and their colleagues at UC San Diego and the New York University Grossman School of Medicine identified the key role of "ZIP-1," a protein called a transcription factor, which helps convert genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA.
The finding, published Jan. 10 in Nature Communications , could have implications for identifying similar genes that control immune responses to infection in humans.
"By better understanding immunity against viral infection we can identify new ways to treat viral infection," said Troemel, a professor in the Section of Cell and Developmental Biology. "The new antiviral factor that we've identified is giving us a better handle on immunity and how worms are fighting off viral infections. Worms sense an RNA virus in a way that's similar to how humans sense an RNA virus like coronavirus."
The researchers studied Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny roundworm with a transparent body that allows scientists to closely monitor how an infection invades a living animal. Lažetić used a fluorescent tracking method to identify which parts of the roundworm's cells are involved in an infection response. He was surprised to find that ZIP-1 emerged so early in the defense process. In addition to viruses, ZIP-1 jumpstarted defenses to infection by a cell-invading fungus as well, the data revealed.
"We found that the subset of genes controlled by ZIP-1 is important for immunity, but not for some other phenotypes that we see in other animals that have activated this immune response," said Lažetić, who noted that the ZIP-1 name comes from its predicted zipper-like structure. "We also observed that ZIP-1 is activated by a previously described receptor that is important for triggering antiviral immunity, both in mammals and in C. elegans, so there are links that can be made with human immunity."
For Troemel, the most surprising aspect of the results was finding that ZIP-1 acts as a centralized hub for immune response against a number of threats.
"A virus, a fungus and heat stress are all so different, but we found that they're all going through the same central ZIP-1 hub to turn on a set of immune genes," said Troemel. "Understanding the early role of ZIP-1 is important because we know that timing matters so much in terms of immune response. That's one of the lessons we have learned with COVID. If you have an early interferon response, that tends to correlate very well with fighting off the infection."
Troemel's lab is now probing the details of the discovery further, including investigating how the receptor that worms use to sense a virus, which is similar to a receptor that humans use in immune response, communicates with ZIP-1 in the defense process.
"Revolutions in biology oftentimes have come from understanding how simple organisms cope with threats such as infection," said Troemel. "Studies that might seem abstract can lead to groundbreaking discoveries."
The Nature Communications paper coauthors include Vladimir Lažetić, Fengting Wu (undergraduate student), Lianne Cohen (graduate student), Kirthi Reddy, Ya-Ting Chang, Spencer Gang, Gira Bhabha and Emily Troemel.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01 AG052622 and GM114139), National Institute of General Medical Sciences/NIH (K12GM068524) and the American Heart Association postdoctoral award (19POST34460023).
